What is a CDN?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a distributed, often global, network of servers designed for quickly serving content. Each datacenter a CDN has servers in is called a Point of Presence (PoP).
What benefits does a CDN provide?
Without a CDN, visitors to your website have to connect directly to the origin server. This server may be on the other side of the world, resulting in a bad user experience for that visitor.
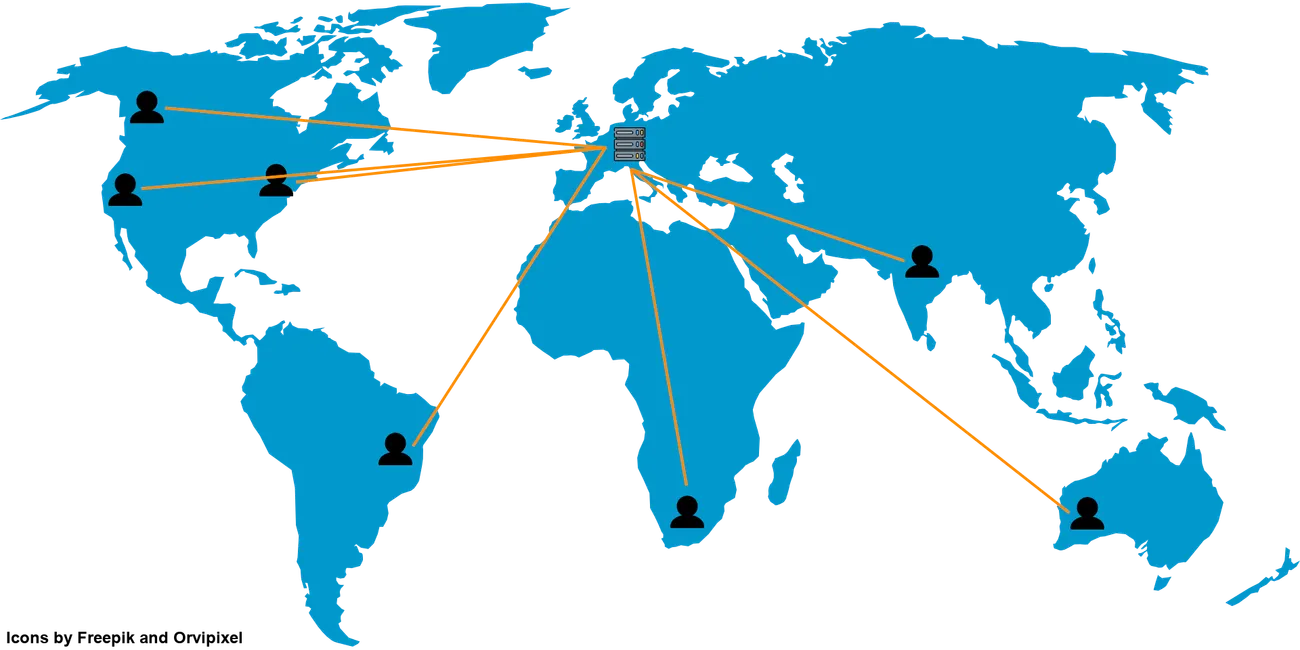
CDNs save a copy of commonly accessed files in each PoP, so that future requests for those files can be served from the PoP instead of going back to the origin server. By moving the website files closer to the user, they can more quickly load the website which improves user experience and customer satisfaction. A CDN also takes load off the origin server, which can reduce hosting costs.
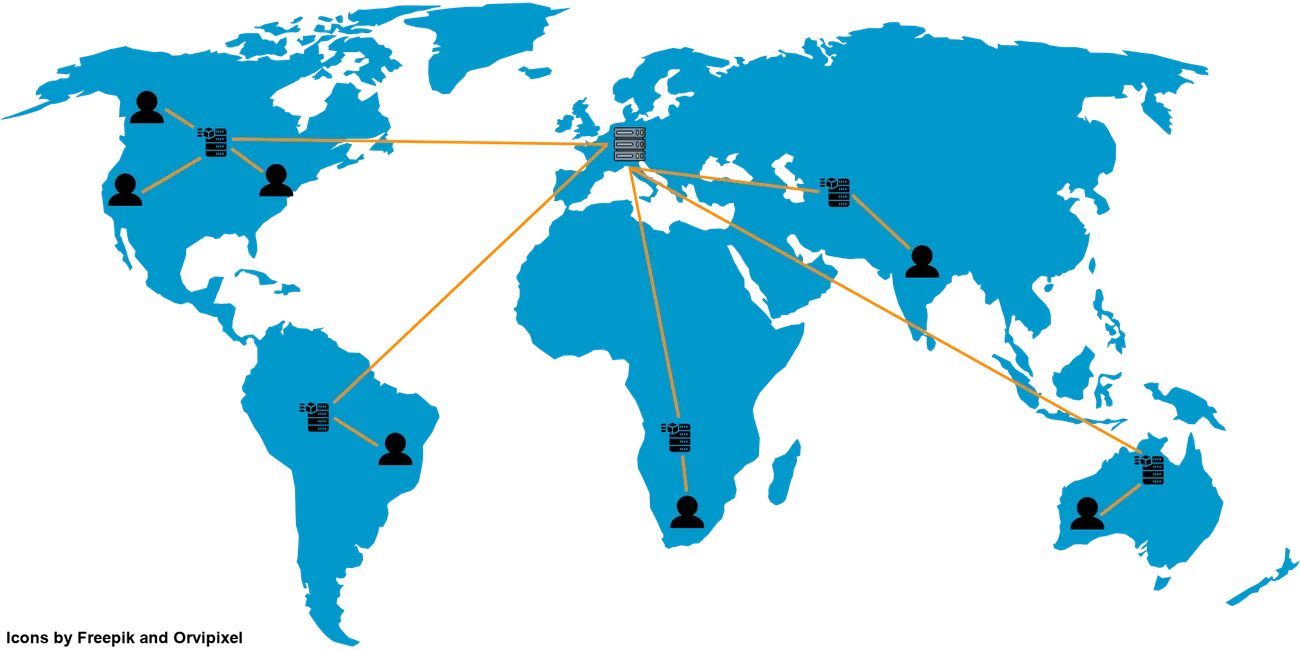
How much does a CDN cost?
CDN pricing differs between providers and is based on:
Visitor location: Most CDNs charge a different price depending on where people access your website from, which can be hard to estimate and budget for
Service quality: Some cheaper CDNs may have a lower service quality or may not have as many PoPs available
Size: Large CDNs are able to negotiate cheaper bandwidth rates and some pass these savings on to customers